Statement of Jeff Chester, Exec. Director, Center for Digital Democracy:
The Federal Trade Commission is supposed to serve as the nation’s leading consumer protection agency. But for too long it has buried its mandate in the `digital’ sand, as far as ensuring U.S. consumer privacy is protected online.   The commission embraced a narrow intellectual framework as it examined online marketing and data collection for this proceeding. Since 2001, the Bush FTC has made industry self-regulation for privacy and online marketing the only acceptable approach when considering any policy safeguards (although the Clinton FTC was also inadequate in this regard as well). Consequently, FTC staff—placed in a sort of intellectual straitjacket—was hampered in their efforts to propose meaningful safeguards.
Advertisers and marketers have developed an array of sophisticated and ever-evolving data collection and profiling applications, honed from the latest developments in such fields as semantics, artificial intelligence, auction theory, social network analysis, data-mining, and statistical modeling. Unknown to many members of the public, a vast commercial surveillance system is at the core of most search engines, online video channels, videogames, mobile services and social networks. We are being digitally shadowed across the online medium, our actions monitored and analyzed.
Behavioral targeting (BT), the online marketing technique that analyzes how an individual user acts online so they can be sent more precise marketing messages, is just one tool in the interactive advertisers’ arsenal. Today, we are witnessing a dramatic growth in the capabilities of marketers to track and assess our activities and communication habits on the Internet. Social media monitoring, so-called “rich-media†immersive marketing, new forms of viral and virtual advertising and product placement, and a renewed interest (and growing investment in) neuromarketing, all contribute to the panoply of approaches that also includes BT. Behavioral targeting itself has also grown more complex. That modest little “cookie†data file on our browsers, which created the potential for behavioral ads, now permits a more diverse set of approaches for delivering targeted advertising.
We don’t believe that the FTC has sufficiently analyzed the current state of interactive marketing and data collection. Otherwise, it would have been able to articulate a better definition of behavioral targeting that would illustrate why legislative safeguards are now required. It should have not exempted “First Party†sites from the Principles; users need to know and approve what kinds of data collection for targeting are being done at that specific online location.
The commission should have created specific policies for so-called sensitive data, especially in the financial, health, and children/adolescent area. By urging a conversation between industry and consumer groups to “develop more specific standards,†the commission has effectively and needlessly delayed the enactment of meaningful safeguards.
On the positive side, the FTC has finally recognized that given today’s contemporary marketing practices, the distinction between so-called personally identifiable information (PII) and non-PII is no longer relevant. The commission is finally catching up with the work of the Article 29 Working Party in the EU (the organization of privacy commissioners from member states), which has made significant advances in this area.
We acknowledge that many on the FTC staff worked diligently to develop these principles. We personally thank them for their commitment to the public interest. Both Commissioners Leibowitz and Harbour played especially critical roles by supporting a serious examination of these issues. We urge everyone to review their separate statements issued today. Today’s release of the privacy principles continues the conversation. But meaningful action is required. We cannot leave the American public—now pressed by all manner of financial and other pressures—to remain vulnerable to the data collection and targeting lures of interactive marketing.
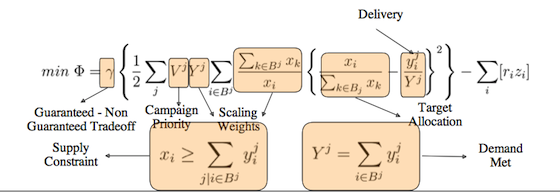 That’s the formula Yahoo is using to please its largest advertisers, explains an article in The Register. The report explains that Yahoo’s economist Preston McAfee has created a “magical formula” for its ad targeting service: “a formula designed to keep Yahoo!’s largest advertisers as happy as possible. It lets each of those guaranteed-contract advertisers pick and choose — in remarkably precise fashion — how their ads are targeted, even though there are more than three trillion possible targets…Yes, Yahoo! has advertisers who only want to reach women between the ages of twenty and thirty. But it also has advertisers who only want to advertise in cities where the sun is shining. There are brokerage houses who only want to advertise when the stock market is up…What is really ‘magic’ about this is that it gave us a backdoor way to price three trillion different pieces of advertiser demand,” McAfee says…The setup also gives Yahoo! fine-grain control over each advertiser’s campaign. “It gives us a dial to favor an advertiser,” he continues. “If one of our advertisers is not getting enough impressions, we turn the dial and increase their bids, to make sure we fulfill the contract.”
That’s the formula Yahoo is using to please its largest advertisers, explains an article in The Register. The report explains that Yahoo’s economist Preston McAfee has created a “magical formula” for its ad targeting service: “a formula designed to keep Yahoo!’s largest advertisers as happy as possible. It lets each of those guaranteed-contract advertisers pick and choose — in remarkably precise fashion — how their ads are targeted, even though there are more than three trillion possible targets…Yes, Yahoo! has advertisers who only want to reach women between the ages of twenty and thirty. But it also has advertisers who only want to advertise in cities where the sun is shining. There are brokerage houses who only want to advertise when the stock market is up…What is really ‘magic’ about this is that it gave us a backdoor way to price three trillion different pieces of advertiser demand,” McAfee says…The setup also gives Yahoo! fine-grain control over each advertiser’s campaign. “It gives us a dial to favor an advertiser,” he continues. “If one of our advertisers is not getting enough impressions, we turn the dial and increase their bids, to make sure we fulfill the contract.”